Internet of Things and Big Data Synergy


Have you heard about the Internet of Things and Big Data? They are two very trending technologies that have evolved independently for a long time but become interrelated over time. Nowadays, people use both these terms together while discussing IoT software solutions or applications.
Technologies have already exceeded human imagination. A usual online graphic calculator available for use from any part of the world is many times more powerful than most computers in the 20th century. In 1976 there was a delivery of the first Cray supercomputer system with more than 5 tons of the total weight of the mainframe! A modern game platform Sony PlayStation 5 which weighs 0,004 tons is more powerful.
The relationship between the Internet of Things and Big Data will impact all spheres of our lives no matter whether you are going to use them during the development of your next software project or as a daily app. We agree with Shawn DuBravac, who wrote in his book about the new age of data: “This is what will happen regardless of which road we take.”
In the article, we consider the Internet of Things and Big Data technologies and discuss how they are interrelated.
Enjoy reading!
Internet of Things and Big Data. Real-life Use Cases
Let us start with real-life examples of IoT systems, where Big Data plays a significant role. The media focuses people’s attention on the mass market side of the Internet of Things development, for example, wearable devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers. However, IoT possibilities are much wider than the functionality of these products, and IoT has a big thing to offer to businesses. Empowered by Big Data and other modern technologies, like cloud computing, nanotech, and IoT systems can be implemented on all levels of business operations in existing companies and even lead to the emergence of new types of businesses that have never existed before. Also with the processing of so much information can help data room for due diligence and data room m&a (mergers and acquisitions) of the large amount of necessary information. Below there are 3 awesome examples of the Internet of Things and Big Data technologies implementation in one system.
Do you believe in miracles? Disney does believe.

Disney decided to use Big Data and the Internet of Things technologies to improve the personal experience of Disney parks. Disney developed Disney’s MagicBand, a colorful, silicone, waterproof wristband that can be used to unlock hotel rooms, enter theme parks, charge food and merchandise purchases. It also collects all sorts of data from visitors and uses it to reduce the waiting time in lines and prepare personalized surprises
Disney spent more than $1 billion to develop a Magical Wristband, and nowadays, it is an indispensable element in the Disney Park magical experience.
Can global Logistics be smart? With Big Data and the Internet of Things, definitely yes
What if a company puts smart sensors in the transportation fleet and calibrates them to record all possible information during the delivery? Will that information be meaningful?
The UPS transportation and logistics company made it and then developed a smart logistics system called ORION based on Big Data collected from sensors. ORION uses advanced algorithms to create optimal routes for delivery drivers from the data supplied by customers, drivers, and vehicles. It also can alter the routes on the fly based on changing weather conditions or accidents.
How can the Internet of Things and Big Data help agriculture?

The crops are vulnerable to damage from insects, disease, and other factors, while agricultural fields are too big for accurate monitoring by humans. Using drones, 3D video sensors, big data, and machine learning, the Aker company enables proactive deep real-time crop observation to mitigate yield loss.
The system is set in two steps: first, drones place video sensors all over the fields. Second, sensors take pictures of crops and make accurate crop health and pest maps of the agricultural fields, allowing farmers to identify crop damage early and make necessary decisions quickly. Sensors continue to work and update maps in real-time.
Aker platform supports more than 50 crop types, the downloading of scouting data offline, and allows sharing of scouting reports. Big Data and the Internet of Things help farmers to decrease damage from pests and pathogens – it’s awesome!
What are IoT and Big Data?
The Internet of Things (or IoT) is a system of interrelated physical devices that can collect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the Internet. A sensor that measures the temperature of the air at home and transfers that information to your smartphone is an element of an IoT system (we have a comprehensive article about IoT architecture).
There are 2 main goals that IoT systems can achieve.
The first one is to provide data from sensors for further analysis by people to help them make the right decision later. For example, fitness trackers collect data regarding your physical activity during the day and advise whether you need to take a little walk in the evening.
Another goal is to provide data to the whole IoT system so the system can make real-time decisions. An example is a driverless car that is outfitted with sensors that collect information about the environment and pass it to the central processor. The system transfers information without any delay allowing the car to make a split-second decision on the road.
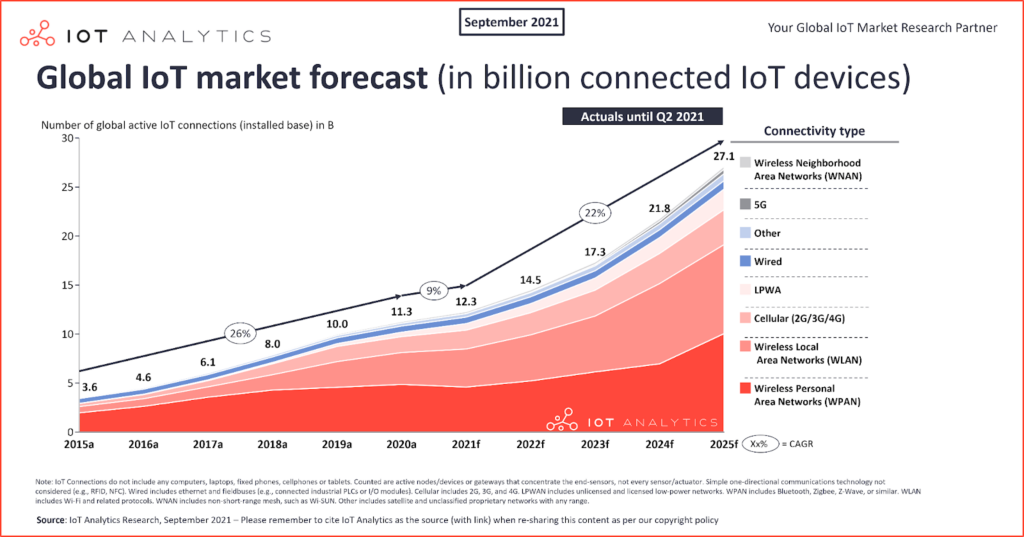
Despite COVID-19’s impact on the global supply chain, the Internet of Things continues to grow, expecting the number of connected IoT devices worldwide to reach 12.3 billion active devices in 2021. IoT showed the world what a fully interconnected world is. We are impressed!
Big Data works with a very large set of structured and unstructured data of different types that is too massive to process using traditional techniques. However, the difference between structured and unstructured data they emerged in big data.
Big Data comprises technologies that help to store, organize, and analyze massive volumes of information.
The main goal of big data is to find patterns in large and unstructured data sets so people can make better decisions and strategic business moves.
We found out what lies behind the terms Big Data and the Internet of Things. But still, the way these two technologies work together is an open question. Let’s clarify it.
What is the relationship between Big Data and the Internet of Things?
The amount of connected IoT devices has already exceeded the world population, and it continues to grow. To complicate things further, IoT today is more about machine-to-machine communication, rather than machine-to-human. That leads to a situation when IoT applications deal with an incredible amount of data that cannot be processed or even stored using traditional methods.
“The rate at which we are generating data is rapidly outpacing our ability to analyze it,” – Dr. Patrick Wolfe, data scientist at the University College of London.
“The trick here is to turn these massive data streams from a liability into a strength.”
In other words, data from IoT devices is only useful when the analysis goes after data collection. So we should concern ourselves with a new question: “How can we learn from data?”
And that question led to a tsunami of Big Data growth that features large-scale applications, an increased amount of machine-to-machine traffic, NoSQL solutions, geographically distributed server nodes, and a large volume of collected data.
Let’s find out how Big Data changes IoT systems.
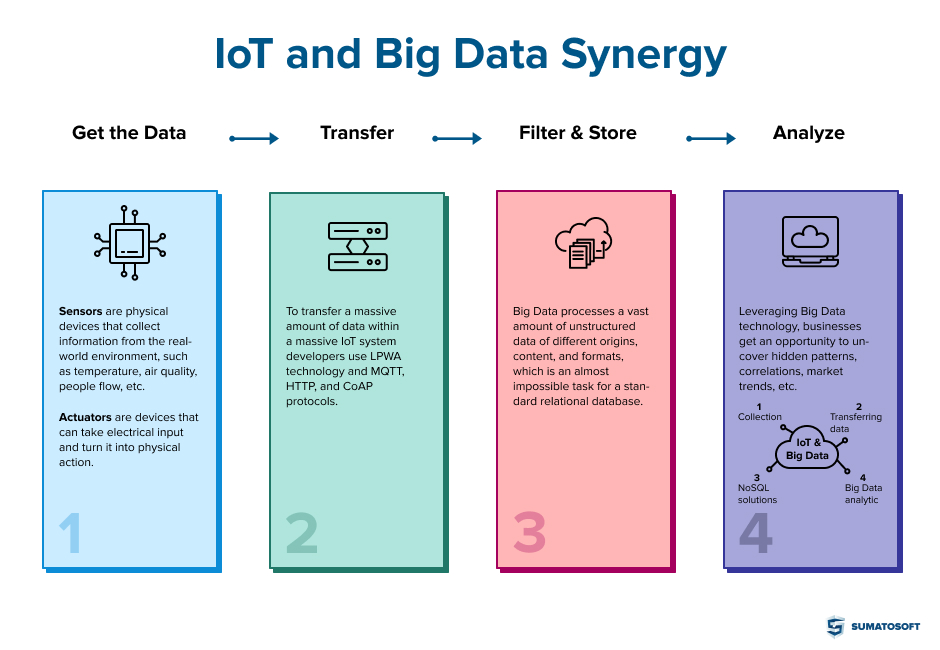
IoT systems include 4 main stages in the architecture that perform varied data manipulations: collection, transferring, filtering and pre-processing, and analyzing. The synergy of Big Data and the Internet of Things impacted 3 out of the 4 stages.
- To transfer a massive amount of data within a massive IoT system developers use LPWA technology and MQTT, HTTP, and CoAP protocols.
- To store the data the only viable option is NoSQL solutions. Big Data processes a vast amount of unstructured data of different origins, content, and formats, which is an almost impossible task for a standard relational database.
- To analyze the data Big Data analytic software comes into play. Leveraging Big Data technology, businesses get an opportunity to uncover hidden patterns, correlations, market trends, etc. The analysis is what allows farmers to identify places with damaged corps, transportation companies to find effective delivery routes, and Disney to provide an unforgettable experience in Disney Park!
At the end of the day, the only thing that matters is how we learn from data to build future-ready solutions.
Conclusion
IoT and Big Data synergy can lead us to new technological applications and complex industrial IoT systems. We are about to see innovations we can only dream of. As new applications enter the mainstream of our daily lives, and technology matures, even more ways to leverage the IoT and Big Data are bound to appear.
FAQ
Is it necessary to use Big Data while building an IoT system?
No. IoT and Big Data technologies are interconnected but still independent of each other. If you have a smart TV, fridge, doorbell, or any other connected device they are a part of an IoT system. However, you don’t need Big Data to realize that you forgot to turn off the light in the bedroom or that your refrigerator is out of milk. Big Data is only needed when it comes to a large number of sensors and massive volumes of unstructured data.
How big is the data in IoT?
According to Statista, the data volume of Internet of Things connections worldwide reached 13.6 zettabytes point in 2021. It’s also expected to reach 79.4 zettabytes by 2025. Even assuming these predictions are half wrong, the numbers are still overwhelming! 1 zettabyte is equivalent to1021bytes (a terabyte is equivalent to 1012bytes). We have entered the new Age of data volume. Welcome to the Zettabyte Era.
Let’s start
If you have any questions, email us info@sumatosoft.com




